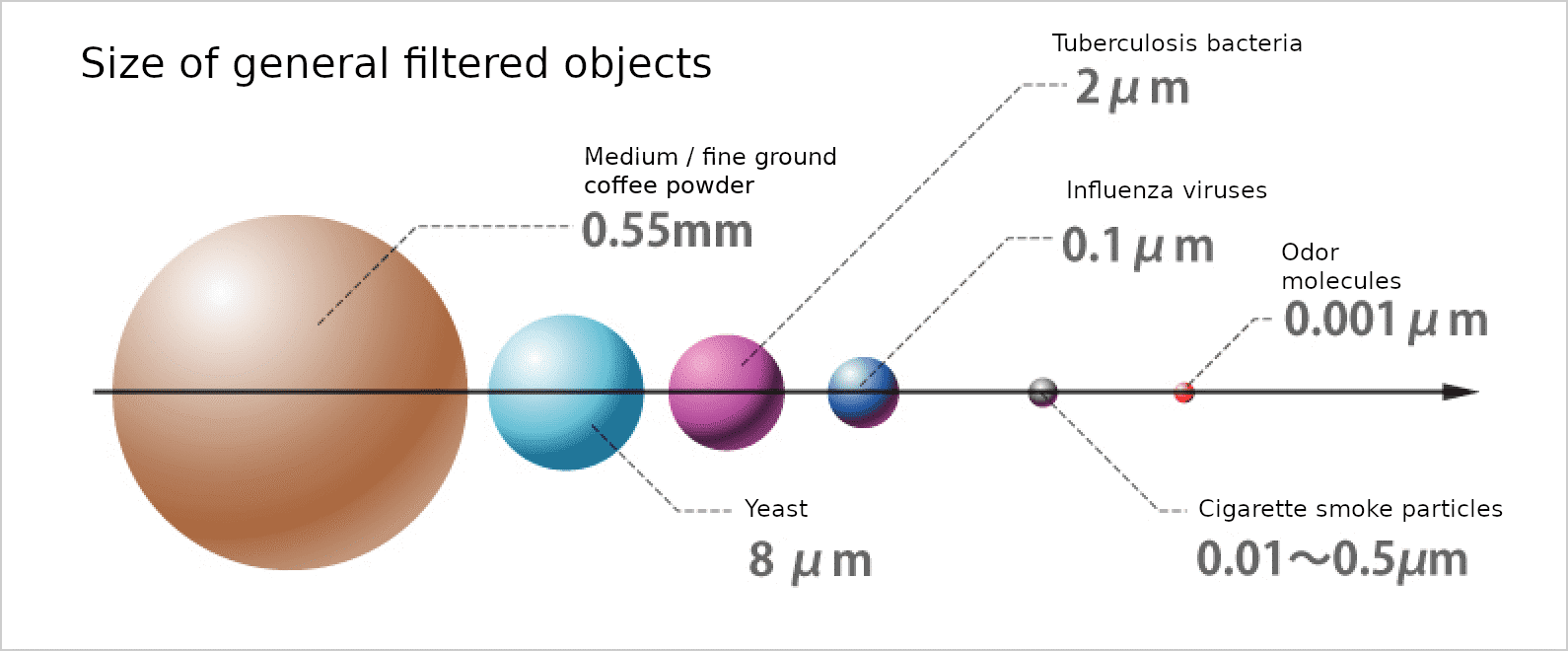
WHAT IS FILTRATION?
What Is Filtration?
Particle removal
Four Main
Mechanisms Of Filtration
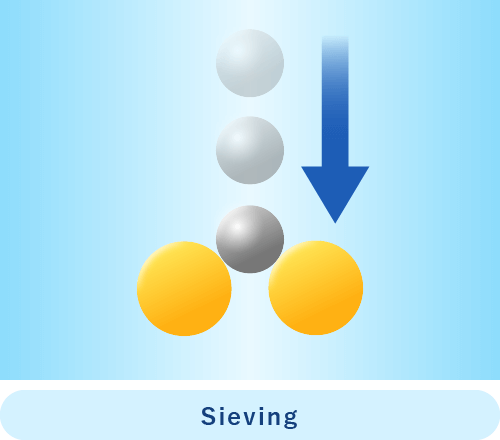
Sieving
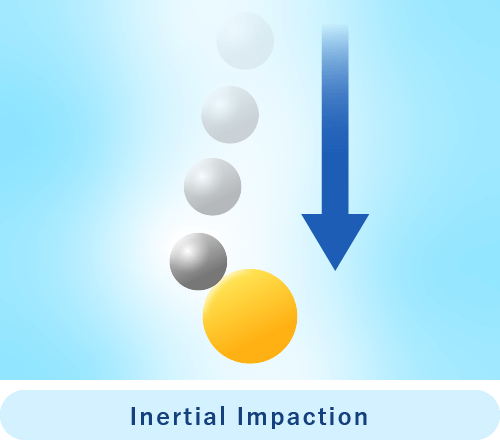
Inertial impaction
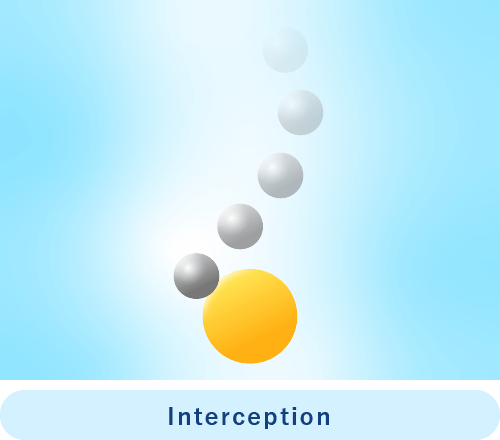
Interception
Diffusion
Sieving
Inertial impaction
Interception
Diffusion
Filtration Techniques
Natural filtration
Performed filtration with gravity only. Although the filtration speed is slower, it is the easiest method because no special equipment is required.
Vacuum filtration
To accelerate speed of filtrating, we decompress the lower surface. It is used to execute filtration quickly with a highly viscous fluid or a large amount of filtration.
Pressure filtration
Pressurized filtration enable to perform with greater pressure, whereas decompression filtration only utilize pressure as the difference from atmospheric pressure,
In addition, there is also a method of applying pressure by using centrifugal force to filter the object to be filtered.
